PingFederate SAML Identity Provider in ZITADEL
This guides shows you how to connect PingFederate as an identity provider in ZITADEL.
In ZITADEL you can connect an Identity Provider (IdP) like PingFederate to your instance and provide it as default to all organizations. Also, you can register the IdP to a specific organization only. If you allow so, your organizations members can do the same in self-service.
PingFederate SAML settings
You need access to a PingFederate administrative console with permission to create SP Connections.
We’ll first configure PingFederate sufficiently to export IdP metadata, which we then import into ZITADEL. After the ZITADEL SAML provider exists, we’ll return to PingFederate and finish the SP settings using the ZITADEL URLs.
Create a new SP Connection for ZITADEL
- Sign in to the PingFederate admin console.
- Go to Applications > SP Connections.
- Select Create New (or Add Connection).
- When asked how to create the connection, choose Manually Configure Connection (do not import metadata yet).
- On the Connection Type screen, choose:
- Browser SSO as the connection type.
- SAML 2.0 as the protocol.
- On General Settings:
- Set a Connection Name, for example:
ZITADEL SAML. - Optionally set an ID or description to identify the connection.
- Set a Connection Name, for example:
Configure Browser SSO
- In the new connection wizard, go to Browser SSO.
- Make sure SAML 2.0 Browser SSO is enabled for this connection.
- Proceed to Assertion Creation:
- Keep the default NameID attribute.
- Add additional attributes you want to send to ZITADEL (you need at least
email,given_name(first name of the user),family_name(last name of the user), and you can send optional attributes likedisplay_name).
- In Attribute Mapping, map the contract attributes to your directory/user store fields.
Export PingFederate IdP metadata
Now export IdP metadata for this connection so ZITADEL can trust PingFederate.
- In PingFederate, go to System > Protocol Metadata > Metadata Export.
- Select SAML 2.0.
- Set the Role to IdP (Identity Provider).
- Choose to generate connection-specific metadata and select the SP Connection you created for ZITADEL.
- Choose a transfer method:
- Metadata URL – PingFederate publishes metadata at a URL you can copy; or
- File download – export the metadata as an XML file.
Keep either:
- the Metadata URL, or
- the XML file contents,
ready for the ZITADEL setup steps.
ZITADEL settings
Go to the IdP providers overview
Go to the settings page of your instance or organization and choose "Identity Providers".
In the table you can see all the providers you have configured. Also, you see all provider templates that are available.
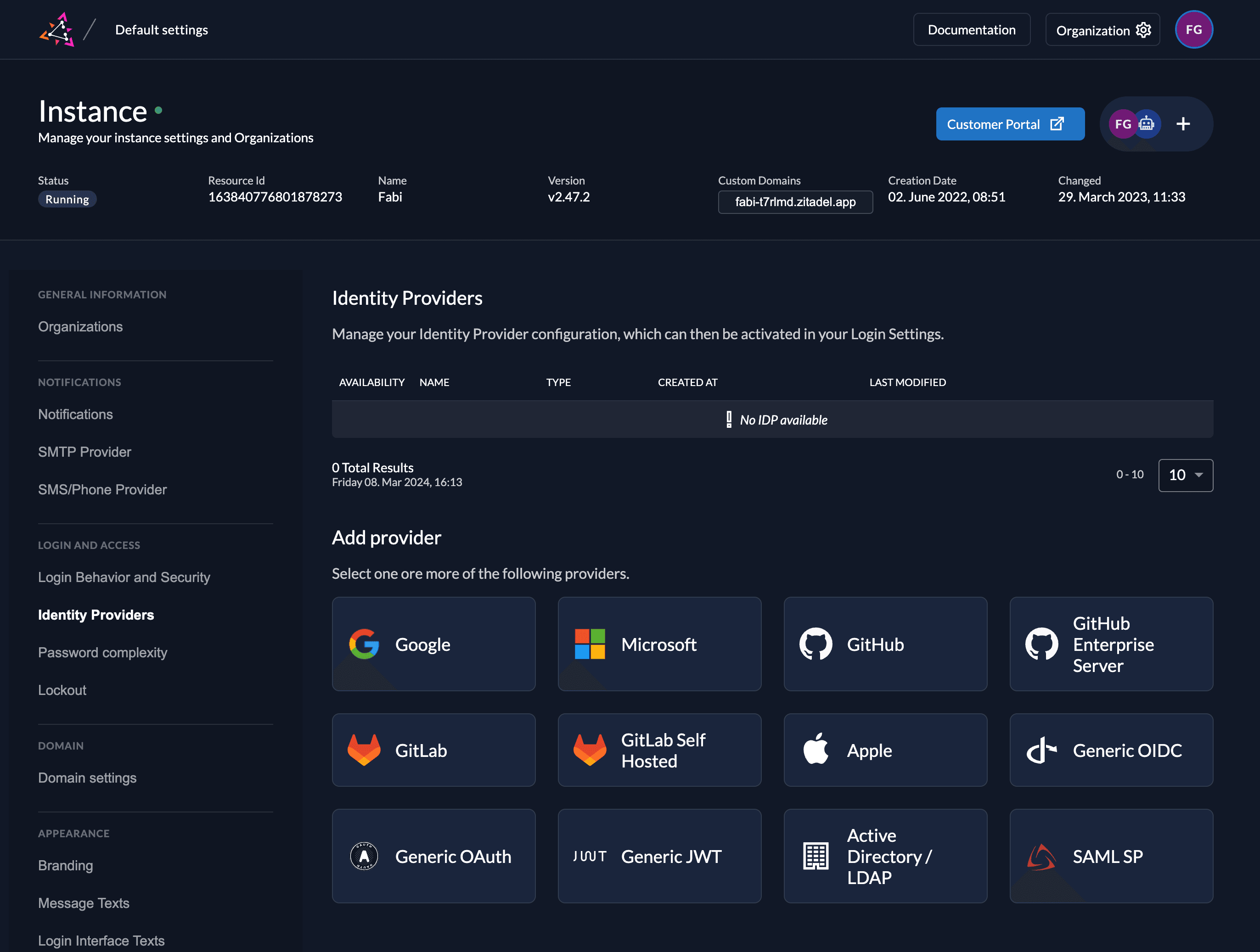
Select the SAML Provider template.
Create a new SAML Service Provider
The SAML provider template has everything you need preconfigured. Add the metadata.xml or the URL to the metadata which are accessible by your ZITADEL instance. All the necessary settings are contained in the metadata which has to be exchanged by the ServiceProvider and the IdentityProvider.
Automatic creation: If this setting is enabled the user will be created automatically within ZITADEL, if it doesn't exist.
Automatic update: If this setting is enabled, the user will be updated within ZITADEL, if some user data is changed withing the provider. E.g if the lastname changes on the PingFederate, the information will be changed on the ZITADEL account on the next login.
Account creation allowed: This setting determines if account creation within ZITADEL is allowed or not.
Account linking allowed: This setting determines if account linking is allowed. When logging in with a PingFederate, a linkable ZITADEL account has to exist already.
Either account creation or account linking have to be enabled. Otherwise, the provider can't be used.
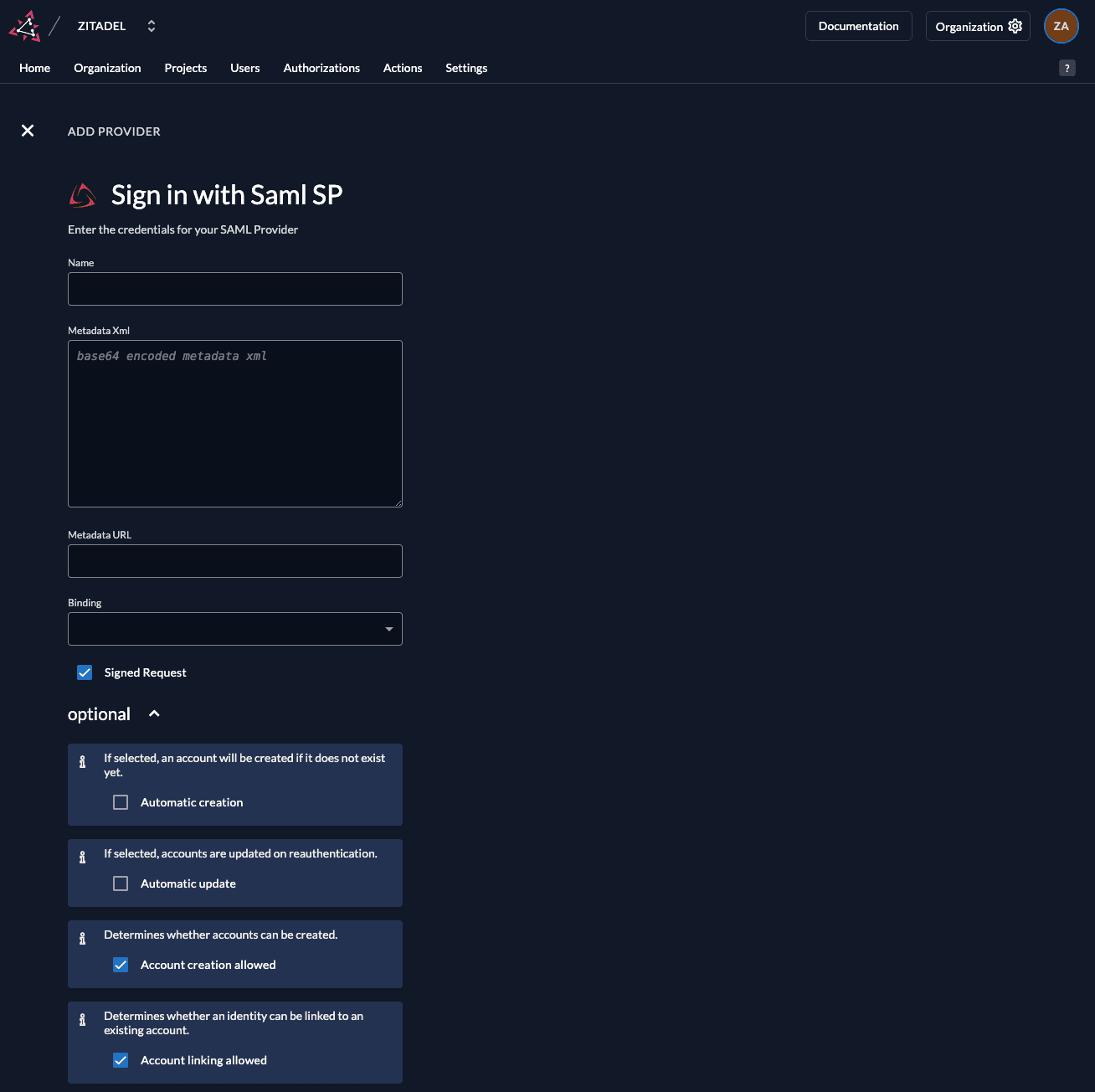
After saving, open the newly created PingFederate SAML provider in ZITADEL. In the details view you will find the ZITADEL Service Provider URLs, such as:
- ZITADEL Metadata URL
- ZITADEL ACS Login Form URL (for Login V1)
- ZITADEL Single Logout URL
- ZITADEL ACS Intent API URL (for Login V2 and programmatic SAML flows)
You’ll need these in the next step.
Import ZITADEL metadata into PingFederate (recommended)
Now that ZITADEL is configured, you can let PingFederate consume ZITADEL’s SP metadata URL. This allows PingFederate to:
- Auto-fill the ZITADEL ACS URL, entity ID, and SLO URLs.
- Import and keep up-to-date the verification/encryption certificates from the metadata.
Create a Partner Metadata URL for ZITADEL
- In the PingFederate admin console, go to: System > Protocol Metadata > Partner Metadata URLs.
- Click Add New URL.
- On the URL tab:
- Name –
ZITADEL SP Metadata(or similar). - URL – paste the ZITADEL Metadata URL you copied from ZITADEL.
- Keep Validate Metadata Signature enabled (recommended) unless you have a reason to disable it.
- Name –
- Click Load Metadata.
- On the Certificate Summary tab, review the certificate information associated with the metadata.
- On the Summary tab, click Done, then Save.
PingFederate can now use this metadata URL to configure and automatically update the SP connection.
Import SP metadata into the ZITADEL SP Connection
With the partner metadata URL defined, apply it to your existing SP Connection for ZITADEL.
- Go to Applications > SP Connections.
- Edit the SP Connection you created for ZITADEL.
- Go to the Import Metadata tab.
- Select URL.
- From the Metadata URL drop-down, select the ZITADEL SP Metadata entry you created.
- If you don’t see it, click Manage Partner Metadata URLs and verify it exists and loads correctly.
- Ensure Enable Automatic Reloading is checked if you want PingFederate to periodically refresh metadata (recommended).
- Click Load Metadata.
PingFederate will:
- Read the SP metadata from ZITADEL,
- Populate the ACS URL, SLO URLs, and other protocol settings for the connection, and
- Import the SP’s signing/encryption certificates for signature verification and encryption.
You can review the updated values on:
- Browser SSO > Protocol Settings (ACS URL, bindings, SLO URLs), and
- Credentials > Signature Verification / Encryption (certificates imported from metadata).
If needed, you can still override specific settings manually, but using the metadata URL is the preferred way to keep endpoints and certificates in sync.
If you need to update the SP Connection with ZITADEL URLs
-
In PingFederate, open the SP Connection you created for ZITADEL.
-
Go to the Browser SSO / Protocol Settings (exact naming may vary by version).
-
Update the SP settings:
-
Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) URL Set this to the ZITADEL ACS Intent API URL from the SAML provider details.
-
SP Entity ID / Audience / Partner Entity ID Set this to the ZITADEL Metadata URL.
-
Single Logout (optional) If you want SAML Single Logout, configure PingFederate’s logout behavior to call the ZITADEL Single Logout URL using the appropriate binding (typically HTTP-Redirect).
-
-
Save and activate the connection changes in PingFederate.
Activate IdP
Once you created the provider, it is listed in the providers overview. Activate it by selecting the tick with the tooltip set as available.
If you deactivate a provider, your users with links to it will not be able to authenticate anymore. You can reactivate it and the logins will work again.
The provider can also be activated via API. As the identity providers are sub-resources of the login settings, this is done by linking the provider to the settings:

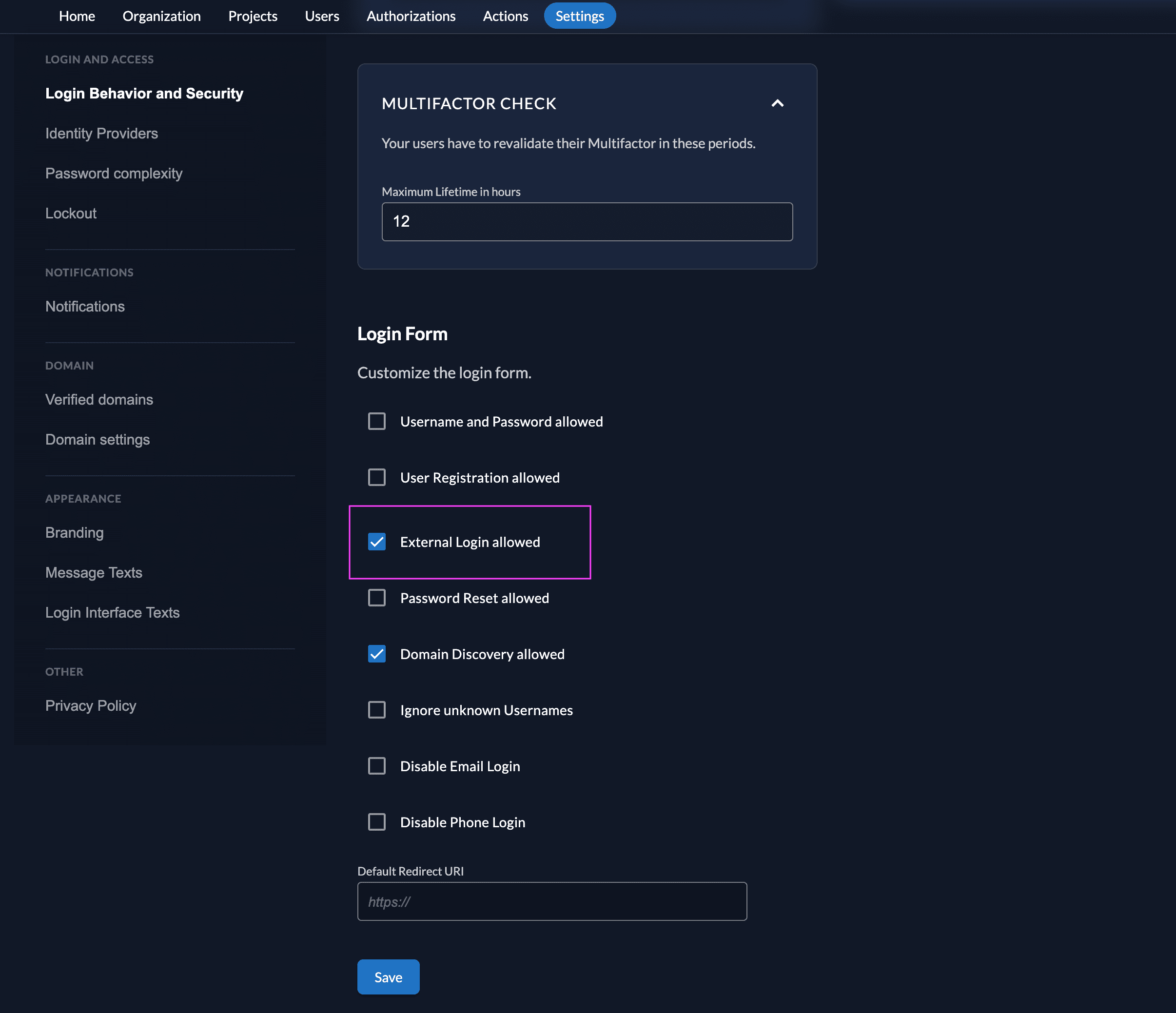
Ensure your Login Policy allows External IdPs
- Go to the Settings
- To allow external IdP logins by default, go to your instance default settings at
${CUSTOM_DOMAIN}/ui/console/instance?id=general - To allow external IdP logins on an organization, go to
${CUSTOM_DOMAIN}/ui/console/org-settings?id=loginand ensure you have the right org context.
- To allow external IdP logins by default, go to your instance default settings at
- Modify your login policy in the menu "Login Behavior and Security"
- Enable the attribute "External Login allowed"
You can also change the settings through the API directly either in the default settings or on a specific organization:
Configure an action to autofill user data
Required for Login V2
The creation of users in ZITADEL will fail if the required fields to create a user are not set.
Actions V2 can be used to map the SAML attributes returned by the IdP to the required fields in ZITADEL. See the Actions V2 Response Manipulation guide for more information on setting up a Target and an Execution. In short,
- Create an Actions V2 Target of type
REST Call - Create an Execution of type
Responseon the method/zitadel.user.v2.UserService/RetrieveIdentityProviderIntent
The following minimal example modifies the response of /zitadel.user.v2.UserService/RetrieveIdentityProviderIntent to set the required fields
for user creation. This is just an example, please adjust the attributes according to your IdP.
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/muhlemmer/gu"
"github.com/zitadel/zitadel-go/v3/pkg/client/zitadel/user/v2"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/encoding/protojson"
)
type contextResponse struct {
Request *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentRequestWrapper `json:"request"`
Response *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponseWrapper `json:"response"`
}
// RetrieveIdentityProviderIntentRequestWrapper necessary to marshal and unmarshal the JSON into the proto message correctly
type retrieveIdentityProviderIntentRequestWrapper struct {
user.RetrieveIdentityProviderIntentRequest
}
func (r *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentRequestWrapper) MarshalJSON() ([]byte, error) {
data, err := protojson.Marshal(r)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return data, nil
}
func (r *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentRequestWrapper) UnmarshalJSON(data []byte) error {
return protojson.Unmarshal(data, r)
}
// RetrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponseWrapper necessary to marshal and unmarshal the JSON into the proto message correctly
type retrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponseWrapper struct {
user.RetrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponse
}
func (r *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponseWrapper) MarshalJSON() ([]byte, error) {
data, err := protojson.Marshal(r)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return data, nil
}
func (r *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponseWrapper) UnmarshalJSON(data []byte) error {
return protojson.Unmarshal(data, r)
}
// call HandleFunc to read the response body, manipulate the content and return the response
func call(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// read the body content
sentBody, err := io.ReadAll(req.Body)
if err != nil {
// if there was an error while reading the body return an error
http.Error(w, "error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
defer req.Body.Close()
// read the response into the expected structure
request := new(contextResponse)
if err := json.Unmarshal(sentBody, request); err != nil {
http.Error(w, "error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// build the response from the received response
resp := request.Response
// manipulate the received response to send back as response
if err = manipulateResponse(resp); err != nil {
http.Error(w, "error modifying response", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// marshal the response into json
data, err := json.Marshal(resp)
if err != nil {
// if there was an error while marshalling the json
http.Error(w, "error marshaling response", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// return the manipulated response
w.Write(data)
}
type rawInformation struct {
Attributes struct {
Email []string `json:"email"`
FirstName []string `json:"firstName"`
Id []string `json:"id"`
LastName []string `json:"lastName"`
} `json:"attributes"`
Id string `json:"id"`
}
func manipulateResponse(resp *retrieveIdentityProviderIntentResponseWrapper) error {
if resp == nil || resp.IdpInformation == nil || resp.IdpInformation.RawInformation == nil {
log.Println("missing IdP/User information in the IdP response")
return nil
}
// retrieve raw information from the IdP
var rawInfoBytes []byte
var err error
if rawInfoBytes, err = resp.IdpInformation.RawInformation.MarshalJSON(); err != nil {
return err
}
// NOTE: the raw information struct used here is just an example.
// Please adapt this to your IdP.
var rawInfo rawInformation
if err = json.Unmarshal(rawInfoBytes, &rawInfo); err != nil {
return err
}
if len(rawInfo.Attributes.Email) == 0 ||
len(rawInfo.Attributes.FirstName) == 0 ||
len(rawInfo.Attributes.Id) == 0 ||
len(rawInfo.Attributes.LastName) == 0 {
log.Println("missing required attributes in the IdP response")
return nil
}
// to create a new user.
if resp.AddHumanUser != nil {
// set the required fields to create a new user in Zitadel based on the information returned by the IdP
resp.IdpInformation.UserName = rawInfo.Attributes.Email[0]
resp.AddHumanUser.Profile = &user.SetHumanProfile{
GivenName: rawInfo.Attributes.FirstName[0],
FamilyName: rawInfo.Attributes.LastName[0],
}
resp.AddHumanUser.Email = &user.SetHumanEmail{
Email: rawInfo.Attributes.Email[0],
Verification: &user.SetHumanEmail_IsVerified{IsVerified: true},
}
resp.AddHumanUser.Username = gu.Ptr(rawInfo.Attributes.Email[0])
resp.AddHumanUser.IdpLinks = []*user.IDPLink{
{
UserName: rawInfo.Attributes.Email[0],
},
}
}
return nil
}
func main() {
// handle the HTTP call under "/call"
http.HandleFunc("/call", call)
// start an HTTP server with the before defined function to handle the endpoint under "http://localhost:8090"
http.ListenAndServe(":8090", nil)
}Test the setup
To test the setup, use incognito mode and browse to your login page. You see a new button which redirects you to your PingFederate login screen.
By default, ZITADEL shows what you define in the default settings. If you overwrite the default settings for an organization, you need to send the organization scope in your auth request.
The organization scope looks like this: urn:zitadel:iam:org:id:{id}.
You can read more about the reserved scopes
or use the ZITADEL OIDC Playground to see what happens with the login when you send different scopes.
Was this page helpful?