Configure private key JWT authentication for service users
This guide explains how developers can use private key JWT authentication to secure communication between service users and client applications in ZITADEL.
In ZITADEL, the urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer ("JWT bearer token with private key", RFC7523) authorization grant type is used for non-interactive authentication.
Read more about the different authentication methods for service users, including their benefits, drawbacks, and security considerations.
How private key JWT authentication works
- Generate a private/public key pair associated with the service user.
- The authorization server stores the public key.
- The authorization server returns the private key as a JSON file.
- The developer configures the client application to use the private key.
- The client creates a JWT assertion with the subject set to the service user and signs the JWT with the private key.
- The client application requests a token from ZITADEL by sending the
client_assertion. - The authorization server validates the signature using the service user's public key.
- The authorization server returns an OAuth
access_token. - The client sends an API request, including the
access_tokenin the Authorization header. - The resource server validates the JWT with token introspection.
Prerequisites
A code library or framework that supports JWT generation and verification (such as pyjwt for Python or jsonwebtoken for Node.js).
Steps to authenticate a Service User with private JWT
Follow these steps to authenticate a service user and obtain an access token for subsequent requests.
1. Create a Service User
- Navigate to Service Users.
- Click on New.
- Enter a username and a display name.
- Click on Create.
2. Register a private key for your service user
You can let ZITADEL generate a private key for you, or upload your own (externally generated) public key. Choose one of the following:
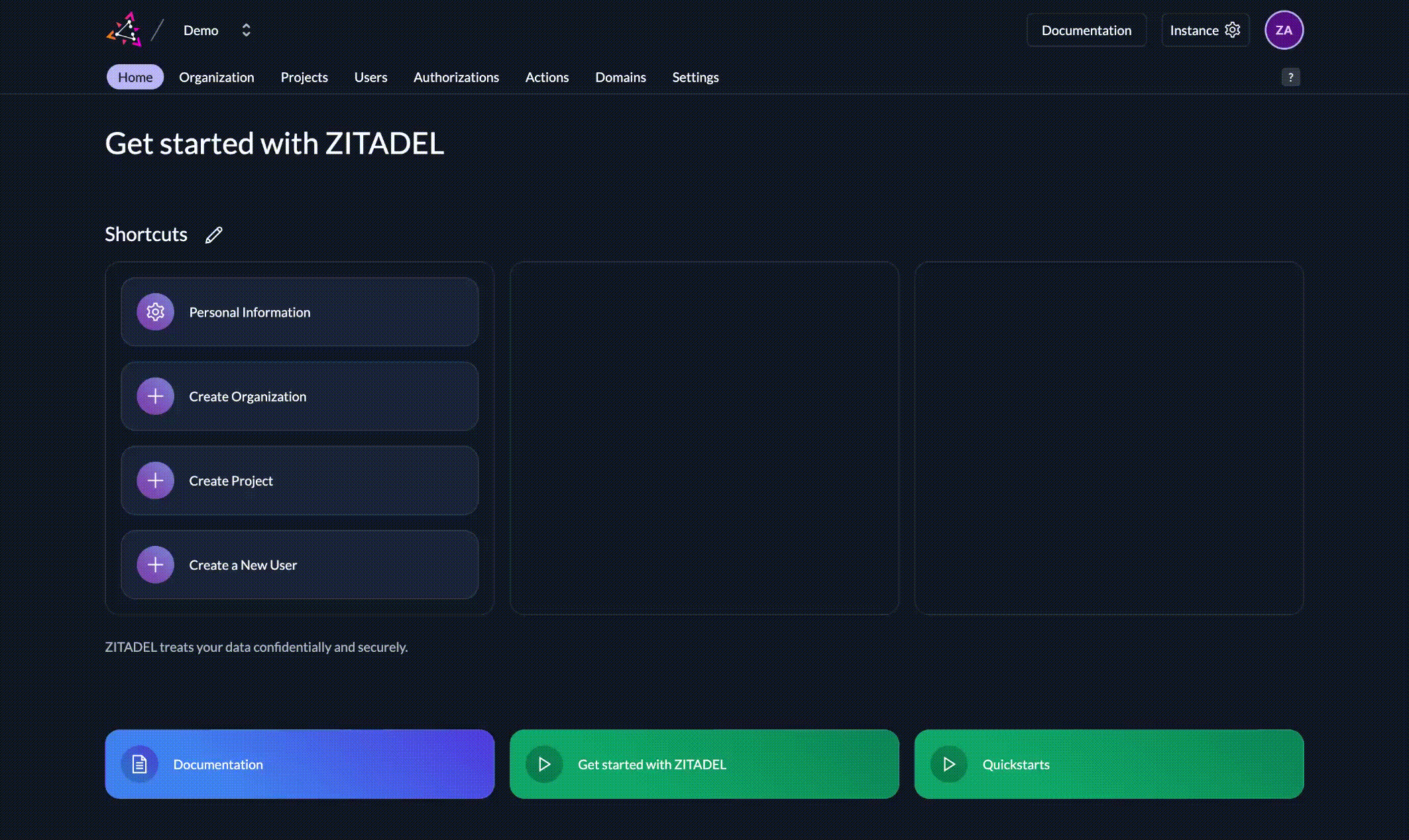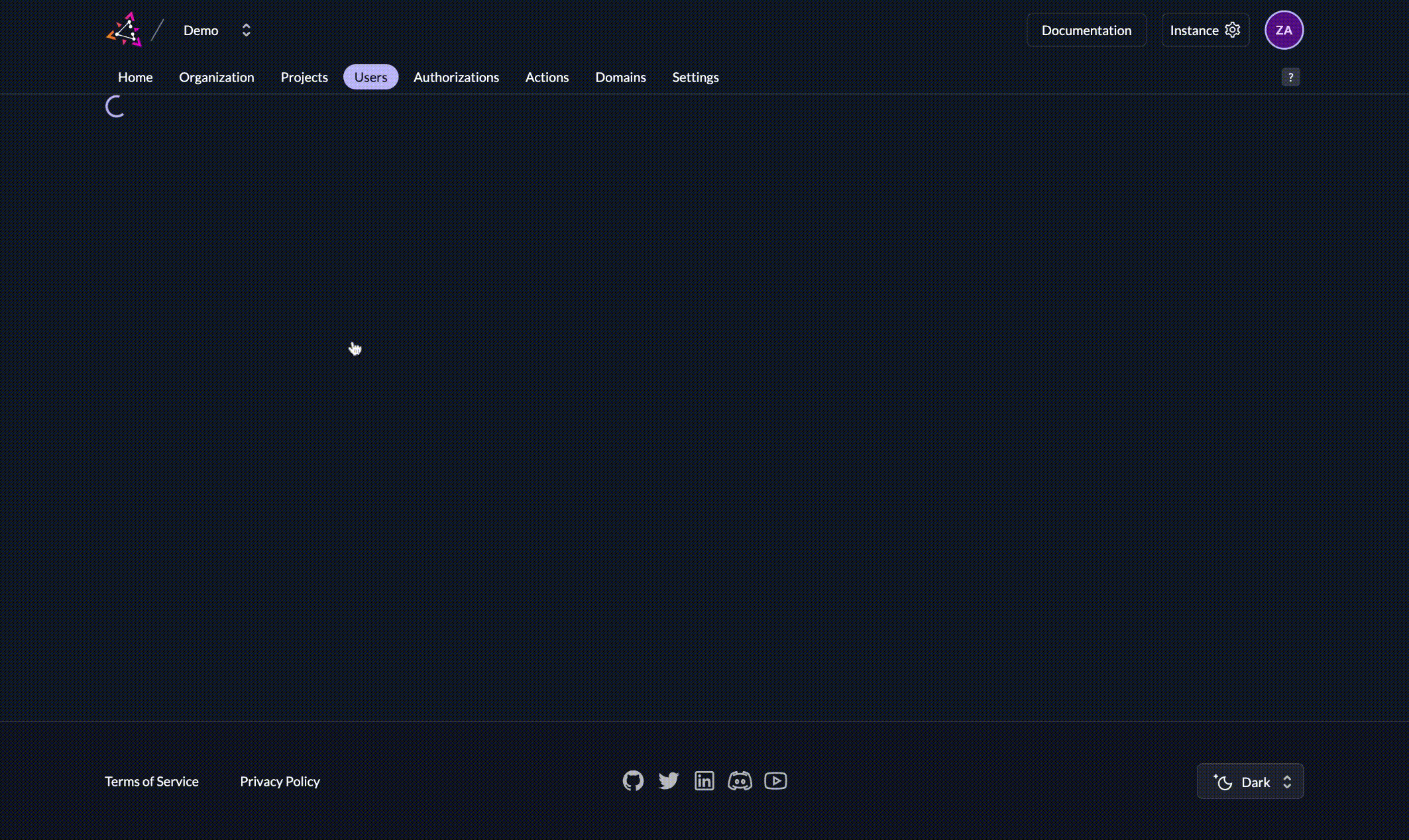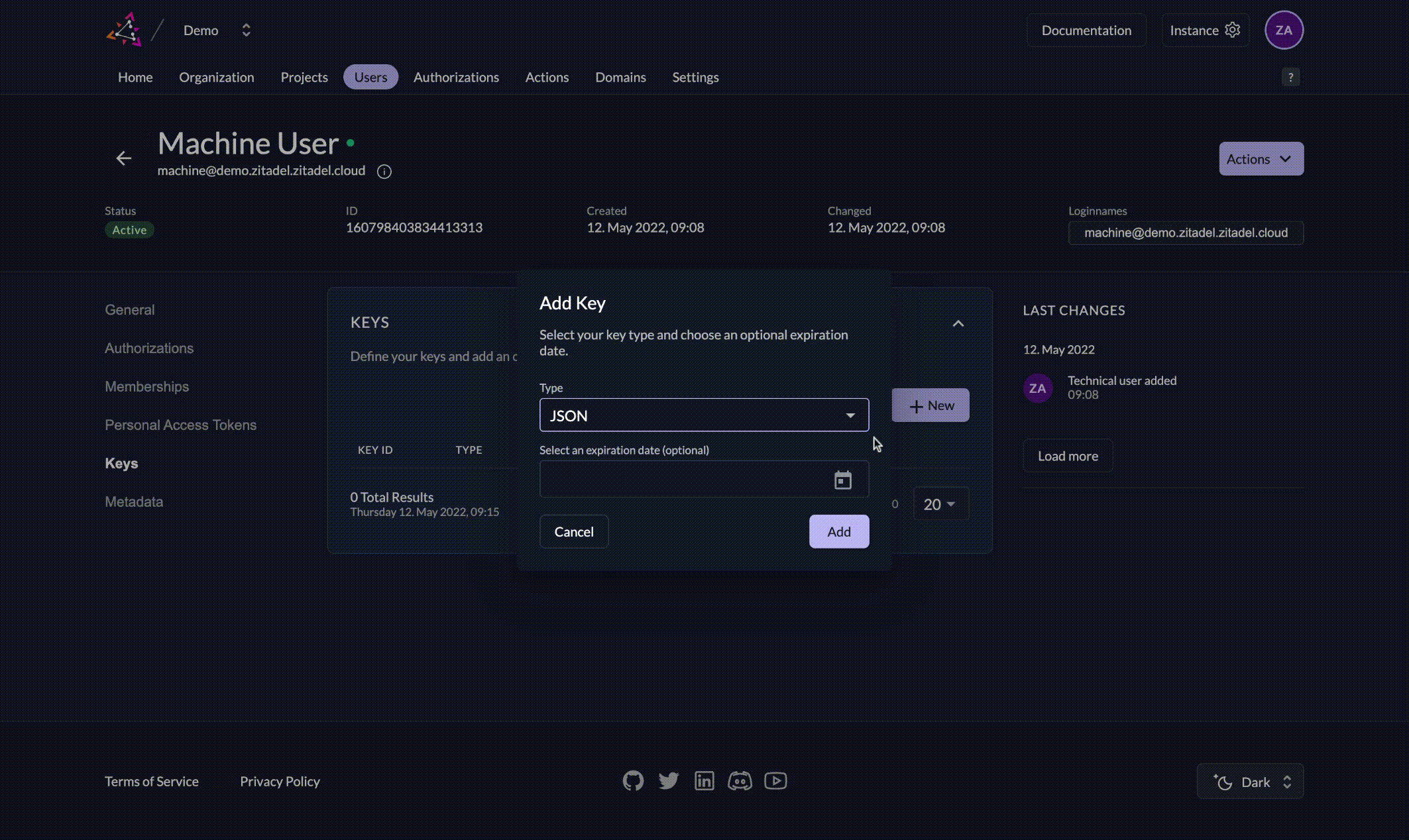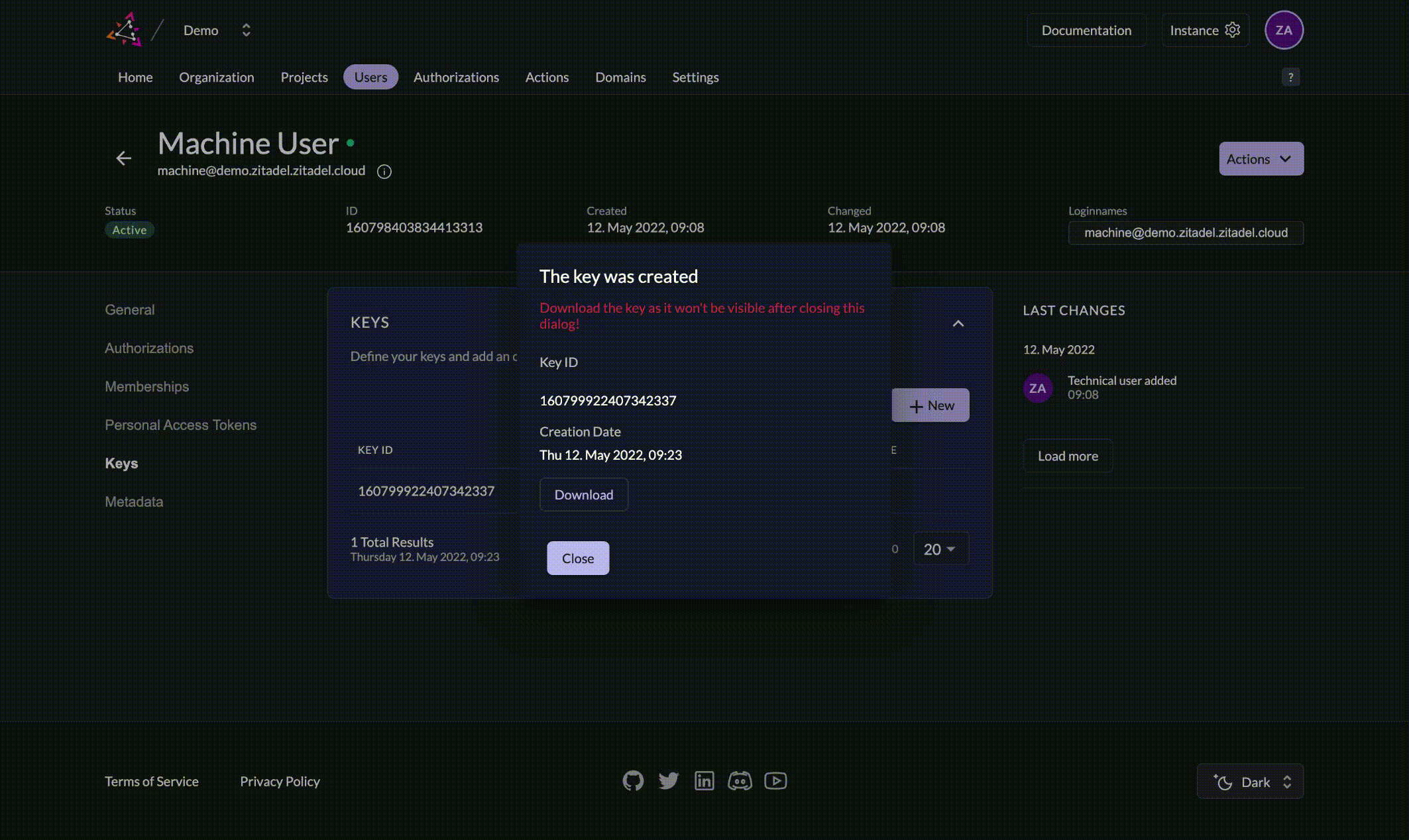
Option A: Generate and download a private key from ZITADEL
- Open the ZITADEL web console and go to your service user.
- Click on the Keys tab.
- Click New.
- Optionally set an expiration date for the key, or leave empty for no expiration.
- Click Download and save the JSON key file securely.
Option B: Register an existing public key for your service user
If you already have a key pair, you can upload the public key for your service user. For example, to generate a key pair using OpenSSL:
# generate key pair
openssl genrsa -out privatekey.pem 2048
# extract public key
openssl rsa -in privatekey.pem -pubout -out publickey.pem
To upload your public key, use the User Service Add Key API
If you generate a key in ZITADEL, make sure to download and securely store the key file right away. For security reasons, ZITADEL cannot show you the private key again after creation. If the key file is lost, you must generate and register a new one.
If you set an expiration date when generating a key in ZITADEL, that key will expire at midnight on the specified day.
If you let ZITADEL generate a key for you and download the JSON file, it will look similar to the example below. In this ZITADEL-generated key file, the key property contains the private key for your service account. Store this JSON securely and never share your private key. ZITADEL automatically stores the public key component, so you do not need to upload it.
{
"type": "serviceaccount",
"keyId": "100509901696068329",
"key": "-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- [...] -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"userId": "100507859606888466"
}
3. Create a JWT and sign it with your private key
You need to create a JWT with the following header and payload and sign it using the RS256 algorithm.
Header:
{
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "100509901696068329"
}
Make sure to include the kid header with the value of keyId from the downloaded JSON.
Payload:
{
"iss": "100507859606888466",
"sub": "100507859606888466",
"aud": "https://$CUSTOM-DOMAIN",
"iat": [Current UTC timestamp, e.g. 1605179982, must be no older than 1 hour],
"exp": [Expiration UTC timestamp, e.g. 1605183582]
}
iss: The entity making the request, i.e., the owner of the private key. Use theuserIdfrom your downloaded JSON.sub: The application. Set this to the same value asuserId.aud: Your Custom Domain.iat: The Unix timestamp when the JWT is created/signed (must be no older than 1 hour).exp: The Unix timestamp when this assertion expires.
For further details, see the JWT with private key API reference.
If you use Go, you can use the provided tool to generate a JWT from the downloaded JSON. There are also many libraries available for generating and signing JWTs.
Code Example (Python using pyjwt):
import jwt
import datetime
# Replace with your service user ID and private key
service_user_id = "your_service_user_id"
private_key = "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nYOUR_PRIVATE_KEY\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----"
key_id = "your_key_id"
# ZITADEL API URL (replace if needed)
api_url = "your_custom_domain"
# Generate JWT claims
payload = {
"iss": service_user_id,
"sub": service_user_id,
"aud": api_url,
"exp": datetime.datetime.now(datetime.timezone.utc) + datetime.timedelta(minutes=5),
"iat": datetime.datetime.now(datetime.timezone.utc)
}
header = {
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": key_id
}
# Sign the JWT using the RS256 algorithm
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(payload, private_key, algorithm="RS256", headers=header)
print(f"Generated JWT: {encoded_jwt}")
4. Request an OAuth token with the generated JWT
With the encoded JWT from the previous step, craft a POST request to ZITADEL's token endpoint:
curl --request POST \
--url https:/$CUSTOM-DOMAIN/oauth/v2/token \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer \
--data scope='openid' \
--data assertion=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiL...
grant_type: Must be set tourn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearerscope: Include any desired Scopes, but must includeopenid.assertion: The encoded JWT you created and signed with your private key.
If you want to access ZITADEL APIs, make sure to include the required scope urn:zitadel:iam:org:project:id:zitadel:aud.
See our guide on how to access ZITADEL APIs for more details.
Important Note: If the service user token must be validated using token introspection, you must include the urn:zitadel:iam:org:project:id:{projectid}:aud scope in your token request.
If you do not include this, token introspection will fail.
A successful response will include the access_token, token_type, and the time to expiry in seconds (expires_in):
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"access_token": "MtjHodGy4zxKylDOhg6kW90WeEQs2q...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 43199
}
5. Include the access token in the Authorization header
When making API requests as the service user, include the generated token in the "Authorization" header with the "Bearer" prefix.
curl --request POST \
--url $YOUR_API_ENDPOINT \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer MtjHodGy4zxKylDOhg6kW90WeEQs2q...'
Accessing ZITADEL APIs
You may use ZITADEL APIs to manage resources (e.g., users) or to validate tokens received by your backend service. Follow our guide on how to access ZITADEL API with your service user.
Token introspection
If your API endpoint receives tokens from users and needs to validate them with ZITADEL, your API must first authenticate with ZITADEL, then perform a token introspection. See our guide on token introspection with private key JWT for details.
Client application authentication
The steps above describe service user authentication. If your application itself also needs authentication, you can use the Client Credentials Grant. See the ZITADEL documentation for additional details on this approach.
Security considerations
- Store private keys securely: Never share or embed the private key in your code or application. Use secure key management solutions whenever possible.
- Set appropriate JWT expiration times: Limit token validity to reduce risk in the event of a compromise.
- Implement proper error handling: Handle cases where JWT verification fails or tokens are expired.
By following these steps and adhering to best practices, you can securely manage service user and client application authentication within ZITADEL using private key JWTs.
